First Reliant Four-Wheeler
Page 50

If you've noticed an error in this article please click here to report it so we can fix it.
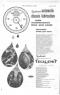
FIRST of a batch of 30 Regent fourwheeled 10-cwt. chassis built by The Reliant Engineering Co. (Tamworth), Ltd., Tamworth, Staffs, for Autocars, Ltd., Haifa, Israel, was shipped in knocked-down units last Saturday, together with the components of a prototype plastics body. A hundred similar chassis, powered by 36-b.h.p. engines, will be supplied to the Israel concern within a few months.
Importers of Reliant three-wheelers for several years, Autocars, Ltd., re-export a substantial proportion of the vehicles to neighbouring countries, notably to Turkey and to a lesser extent to Greece, Somalia and Ethiopia. The new vehicle was designed specifically to meet a demand for a four-wheeler which could he assembled in the country and equipped with bodies built by Autocars.
Initially, replicas of the prototype resin-bonded glass-fibre body will be produced for the vehicle using working moulds supplied by the chassis maker's. This, it is claimed, will be the first example of a plastics body being made in Israel.
Later, other forms of plastics body will he built in Haifa, including stationwagon and private-car types. It is believed that the latitude provided by glass-fibre construction will enable modifications to be made to suit the requirements of individual customers at a relatively small cost. The prototype body is based on a hardwood frame.
The size and performance of the fourwheeler are such that the vehicle will be marketed in direct competition with vans produced in quantity by the larger manufacturers, and the advantage of offering a cha!,sis with a separate frame which can B16 be fitted with locally made bodies is, therefore, important.
Although the use of a conventional frame gives a slightly increased chassis weight, that addition is more than offset by the weight saving resulting from employing a plastics body. The chassis weight is just under 71: cwt. and it is expected that with standard body the complete vehicle will weigh less than 13 cwt.
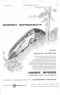
Of 1,172 c.c. capacity, the engine is a well-tried fourcylindered side-valve unit • and develops its rated output of 36 b.h.p. at 4,400 r.p.m., with a peak torque of 52 lb.ft. at 2.500 r.p.m. It has a compression ratio of 7 to and is supplied by a 6-gal. fuel tank Power is transmitted by a single dryplate clutch and three-speed synchromesh gearbox through a needle-jointed propeller shaft to a spiral-bevel rear axle. The overall top-gear ratio is 5.14 to I, whilst second and bottom ratios are 9.57 to 1 and 17.48 to I respectively. Reverse has a ratio of 22.87 to 1.
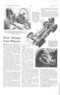
Chassis-frame design is generally similar to that of the standard threewheeler, in that flanged box-section main members of 16-gauge material are employed in conjunction with tubular cross-bracing members.
A deep box-section cross-member at the front gives rigid support for the independent front suspension, which is give lateral stability. The shackles incorporate Silentbloc rubber bushes.
• Pressed-steel wheels with wide-base rims carry 5.60 by 15-in, tubeless tyres. General dimensions include a wheelbase of 7 ft. 1 in. and an overall chassis length of 11 ft. 4 in. The front track is 48 in., whilst the rear track is 49 in. Overall chassis width is 4 ft. 64: in. and the vehicle has a ground clearance of 8 in. The
• turning circle is 30 ft.
• Hydraulically actuated brakes operate in 7-in. by 1+-in, drums at both the front and rear. Leftor right-hand steering may be specified, the steering box being of the Burman-Douglas type.
The Regent four-wheeler will later be marketed in this country.