New All-alloy • Jig-built I Bus-Bodies
Page 36
Page 37

If you've noticed an error in this article please click here to report it so we can fix it.
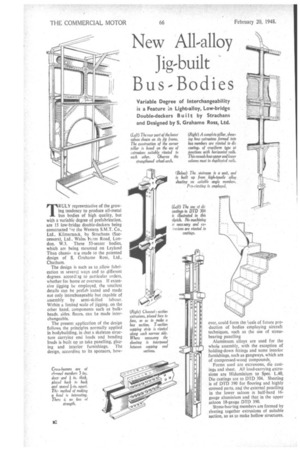
TRULY representative of the growing tendency to produce all-metal bus bodies of high quality, but with a variable degree of prefabrication, are 15 low-bridge double-deckers being constructed l'or the Western S.M.T. Co„ Ltd., Kilmarnat, by Strachans (Successors), Ltd., Wales Pi rm Road, London, W.3. These 53-seater bodies, which are being mounted on Leyland Titan chassi?, are made to the patented design of S. Grahame Ross, Ltd., Chatham.
The design is such as to .allow fabrication in several ways and to different degrees accordi3g to particular orders, whether for home or overseas If extensive jigging be employed, the smallest details can be prefab icated and made not only interchangeable but capable of assembly by semi-skilled labour. Within a limited scale of jigging, on the other hand, components such as bulkheads. sides. floors, can be made interchangeable.
The present application of the design follows the principles normally applied in bodybuilding, in that a skeleton structure carrying end loads and bending loads is built up to take panelling, glazing and interior furnishings. The design, accordinq to its sponsors, how ever, could form the basis of future production of bodies employing aircraft techniques, such as the use of stressbearing panelling Aluminium. alloys are used for the whole assembly, with the exception of holding-down fittings and some interior furnishings, such as gangways, which are of compressed-wood compounds.
Forms used arc extrusions, die castings and sheet. All load-carrying extrusions are Hiduminium to Spec. L.40. Die castings are to DID 304. Sheeting is of DID 390 for flooring and highly stressed parts, and the external panelling in the lower saloon is half-hard 16gauge aluminium and that in the upper saloon 18-gauge DTD 390.
Stress-bearing members are formed by riveting together extrusions of suitable • section, so as to make hollow structures.
During this process, allowance is made for the subsequent securing of interior and exterior panels. Glazing is carried out externally by means of self-contained winclJws and pans.
Where members intersect, e.g., where rails meet pillars, the extrusions are broken and continuity is preserved by four'-wa., die castings fitting inside the hollow metnbers and pop meted to them.
Almost the entire assembly, down to details, is carried out with the use of pop rivets of the break-stem type. Solid rivets are used, however, on the cross-bearers.
Cross-bearer construction is interesting. Eacli bearer ce.isists of two extruded channels placed back to back and spaceJ f in. apart. The section is 3 ins, deep with I-in, flange, and is
in. thick At each end a casting, secured by solid l-in. rivets, takes the channel sections for the main pillars and the bottom rail.
Front and rear bulkheads, designed for great strength and rigidity, are of similar construction, in that they consist of framed structures, on each side of which is riveted the sheeting. The front bulk head comprises corner pillars, roof beam, cross-beam at the waist, chassis supporting struts, and details, such as bracing channels and .crib angles. When plated, this forms a robust structure. It is held to the chassis by steel eyebolts built into the struts.
The rear bulkhead has a pair of straight cross-members at the bottom, from which are suspended the holdingdown bolts Entranc posts are fixed to the cross-members by machined fittings riveted to the posts and bolted through the channels.
A heavy-gauge plate along the bottom edge serves as a riser. At the top is a roof beam to take the upper saloon floor. The off side is cut away and reinforced for the rear end of the well girder.
Saloon Sides are Units
Lower-saloon sides are complete structures, from cant-rail to valance brackets. As ons.ts, they are offered up to the bulkhead corner pillars and fixed by pop rivets At the wheel-arch cutaway the side framing is reinforced by diagonal bracers and internal sheeting. Construction of the upper saloon follows the same lines, the main difference being the smaaer size of pillars and rails.
Top-hat-section stiffeners run the length of the lower floor and are riveted
to the bearers. Intermediate crossstiffeners are incorporated. Seatpedestal support rails are extrusions, and pedestal bolts screw into' blocks riveted inside the sections. The AlcIad I6-gauge covering is riveted to the stiffener flanges.
The upper floor follows the same principles, but extends beyond both bulkheads, whilst the front part of the canopy is separately fixed. On the off side the floor is supported by the stepwell girder, which ends at each bulkhead Flooring in the well is of labroc—a compressed and impregnated form of laminated wood.
The method of joining upper and lower complete saloon is important. Lower-saloon cant-rali castings have vertical lugs on the inside, to meet thickened bosses on the upper-saloon bottom-rah castings. A bolt is put through the lug and boss at each pillar, whilst the joint is finished by riveting the two rails inside and outside by metal strips under the headings.
Holding-down fittings are stout angles bolted to the main frame and slotted to take eyebolts on the structure. The slots allow wide tolerance. A steel clamp bridges the slot and takes the thrust of the nut when tightened.
Slung from the upper deck and front bulkhead, the cab is separate from the radiator and bonnet. The off-side upper-deck structure over the cab is reinforced by internal sheeting, to prevent any possible droop.
The rear platform is supported by the chassis extension and the whole of the exposed surface is of non-slip material.
There is wide use of Holoplast—a compressed and resin-bonded sheet—in the lower saloon. It is used for seat squabs and seat supports. In the case of the back squabs, it is built into metal channelling, of which the open portion is hard-wood filled, to take upholstery pins. This is. in fact, the only use of timber in the whole body.
Holoplast is used as trimming below the waist rail The sheets are fixed to the strips of metal between pillars and rails by Rivnuts and recessed head screws. , Lining sheets of this material are also fitted to the lower-deck roof between the cove panels.
Emergency Window Seal
An orthodox emergency window is fitted at the rear of the upper deck. but it has a simple and effective rattleproof sealing device.
Life guards are of heavy-gauge alloy tube of oval section.
It is interesting to consider the reasons fri,' adopting light-alloy construction ,n these buses, as given by the designer. Use of metal, as opposed to wood is, of course, largely a matter dictated by current condition, although the all-metal bus has many advantages.
Light-alloy sheets, extrusions and castings, it is stated, result in more robust sections than those of their equivalents in steel. Presumably, the designer means that a more satisfactory balance may be struck between strength and weight. An extruded-alloy section, it is mentioned, allows the metal to be distributed to the maximum advantage, whereas in wood this can be done only by• craftsmanship and complicated spindling operations. In steel, the same sections would be approximately one-third of the thickness of the alloy which takes their place, and would be difficult to handle and costly to work, because of the light section.
Simplicity end cheapness are claimed as outstanding advantages of using extrusions and castings. All extrusions employed 'as structural members arrive from the metal industry ready for use, apart from cutting to length. The small amount ot manipulaaon to shape needed for deck beams is easily carried out, but even this could be arranged with the supplier of the extrusions. The die castings employed to join the sections together are also ready for use without machining.




















































































